Teamspace Setup
Teamspaces are vanilla Kubernetes clusters with Codezero installed. The following guide will step you through registering a Teamspace and certifying it for development use. This should take about 10 minutes to complete.
Create a Codezero Hub Account
Sign up or log in to the Codezero Hub. The onboarding wizard will guide you through creating an organization and your first Teamspace.
The Hub allows you to register and certify Teamspaces. This is also where you can invite and administer members of the Teamspace. While the Hub provides a graphical user interface equivalent to the czctl command line tool, all services either run on your local machine or in the Kubernetes cluster.
Install Codezero in your Cluster
On the Profile menu, click Settings and then select Teamspaces. Click Add Teamspace to create the installation command.
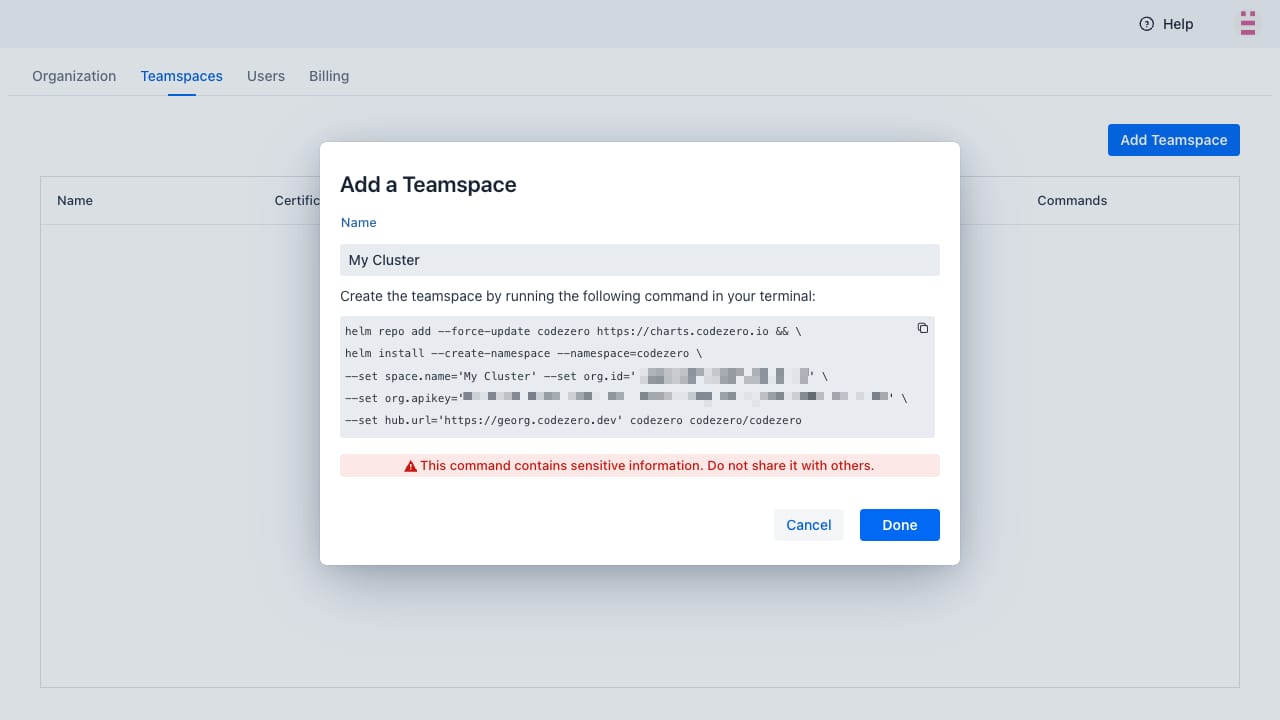
This install command contains your organization's API key. Please keep it confidential. It uses Helm to install the Codezero Space Agent. You can find the Helm charts on Codezero's GitHub.
Additional annotations may be necessary; refer to our Codezero Helm Chart documentation and the section on Load balancer requirements below.
Load balancer requirements
The Codezero helm chart deploys a Kubernetes service of type LoadBalancer. For Codezero to function properly the provisioned load balancer requires a public ip address and must work on OSI layer 4.
- AWS EKS
- GKE
- Generic cluster
By default AWS EKS uses classic load balancers for a Kubernetes service of type LoadBalancer. In this case no additional setup is required.
However when using AWS Load Balancer Controller additional annotations need to be set on Codezero's load balancer service. This can be done via the helm chart by adding the following values:
lb:
service:
annotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: "external"
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-nlb-target-type: "ip"
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-scheme: "internet-facing"
Google Kubernetes Engine creates external Network Load Balancers by default.
Codezero will rely on the default behaviour provided by the cluster.
Certification
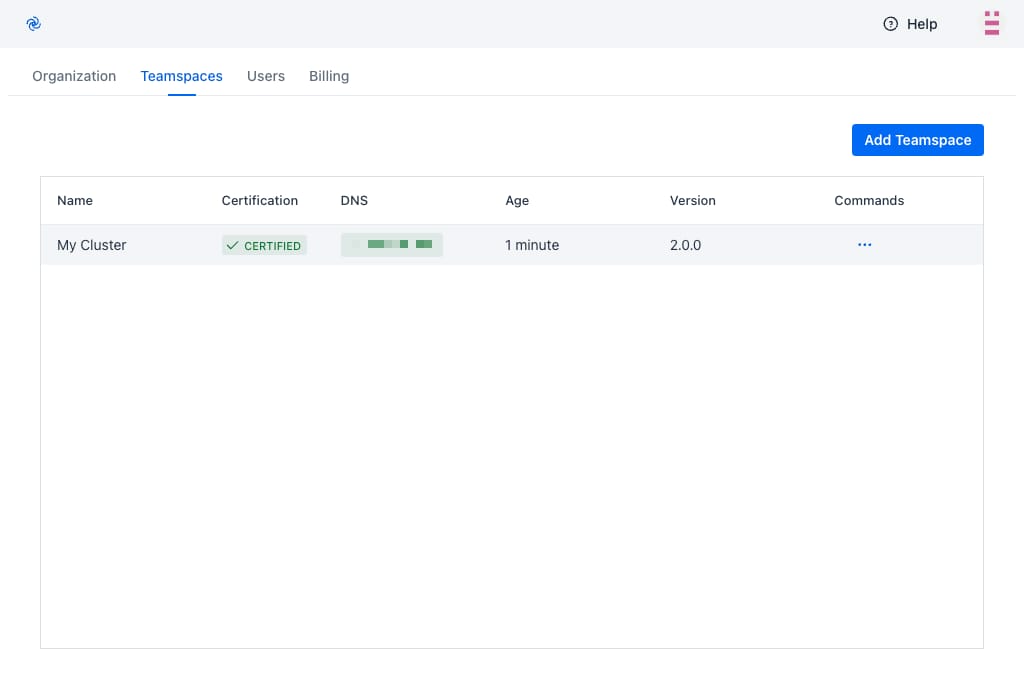
The Codezero System installs into the codezero namespace and should take less than a minute to start depending on how long it takes to provision a LoadBalancer. Once ready, you should see the Certification column change to Certified and shortly thereafter, you should see an IP address or Host Name show up under DNS. Your Teamspace is ready for use.
Certification ensures secure communications between the Codezero System in cluster and the Hub.
You can now select the Teamspace from the Teamspace List in the navigation panel. This will take you to the Service Catalog:
Uninstalling Codezero
Codezero may be removed from the Kubernetes cluster at any time. It is recommended that you close all Consume and Serve sessions before you begin the uninstallation.
To uninstall, run:
helm -n codezero uninstall codezero
You can then go into the Hub and delete the Teamspace.
Troubleshooting
Upgrade Cluster / Codezero Space Agent
Occasionally a new Codezero release requires you to Update your Codezero Space Agent (also referred to as Upgrade your Cluster)
To update your Codezero Space Agent, run the following command:
helm repo add --force-update codezero https://charts.codezero.io && helm upgrade --namespace=codezero codezero codezero/codezero`
Stuck Waiting for DNS
The Codezero System service will fail to start if it is unable to obtain the DNS address of the cluster. Sometimes, the Kubernetes retry logic will time out before the ingress is ready. In this case, you may have to restart the System service. To do so, simply delete the System pod:
kubectl -n codezero delete pod system-<RANDOM>
Locating Codezero Residue
Codezero does not use any Custom Resource Definitions or finalizers. In the event that you need to lookup resources added or modified by Codezero, you can use the following kubectl commands
kubectl get all --selector="app.kubernetes.io/managed-by"=codezero --all-namespaces
If you are looking for residue in a specific namespace, use:
kubectl -n <NAMESPACE> get all --selector="app.kubernetes.io/managed-by"=codezero
You should close all Consume and Serve sessions prior to cleaning up residue in which case the Codezero System controller will perform the cleanup for you. If for whatever reason, it does not, you can remove the resources found and re-deploy your application to get back to a clean state.
Getting Further Help
If you have any further questions - please reach out to us via support@codezero.io or Discord or your dedicated Slack Connect channel (if you're an Enterprise Customer).